About
About This Instant Demo
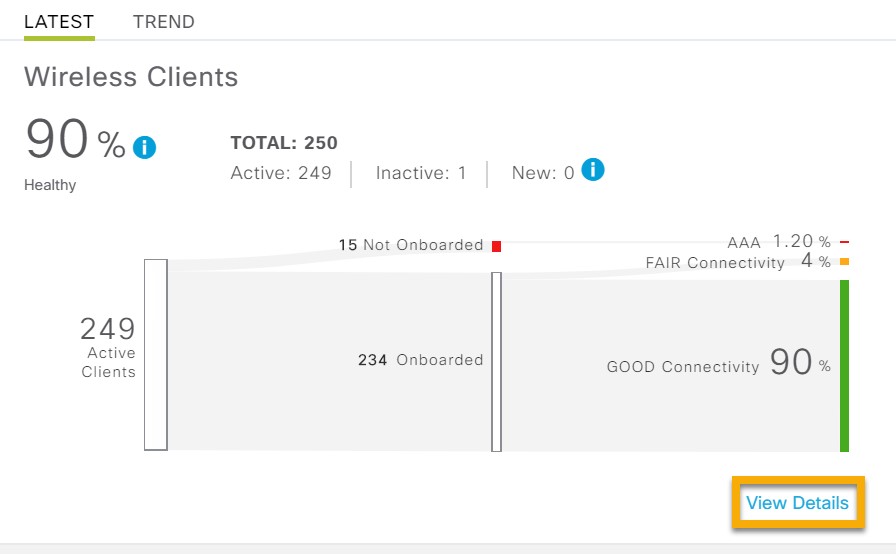
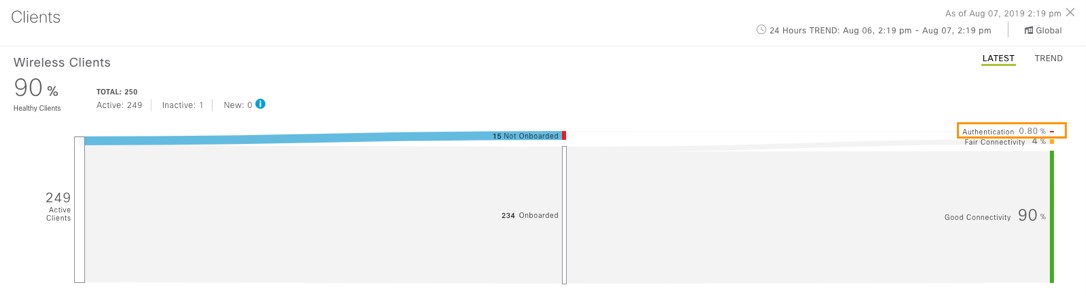
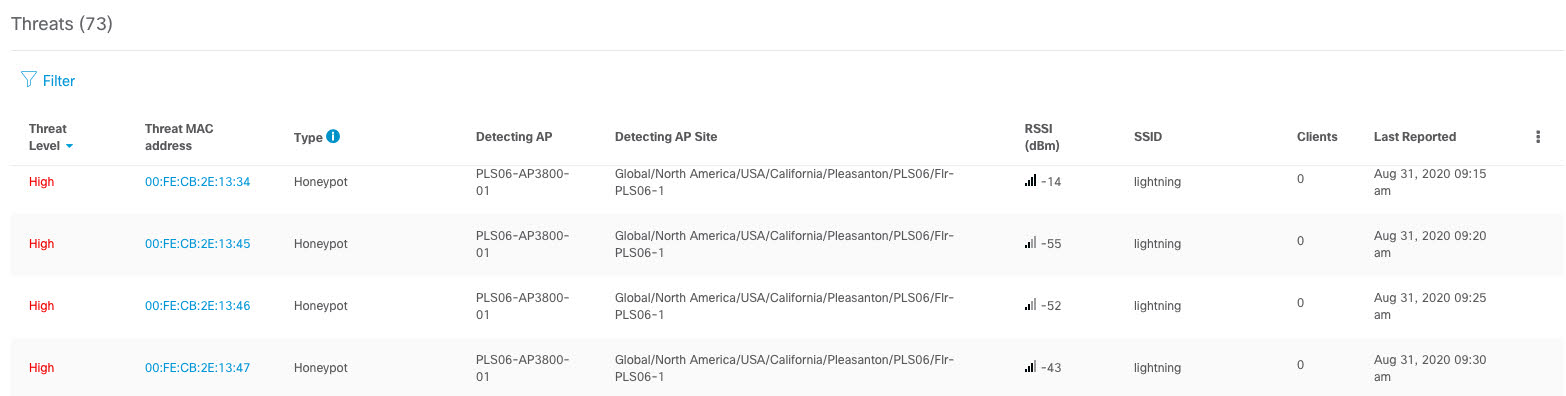
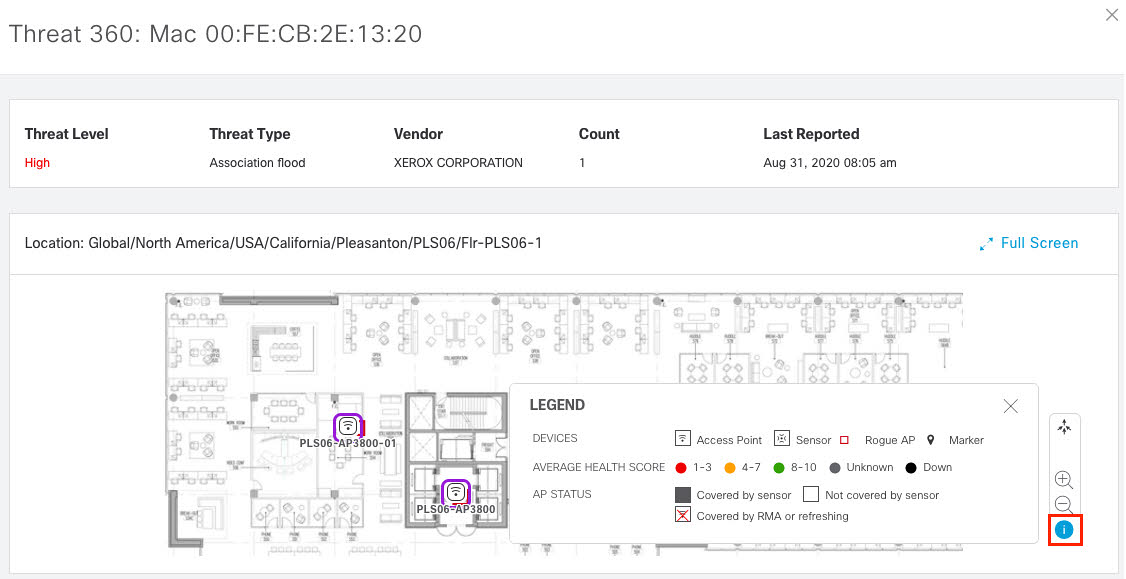
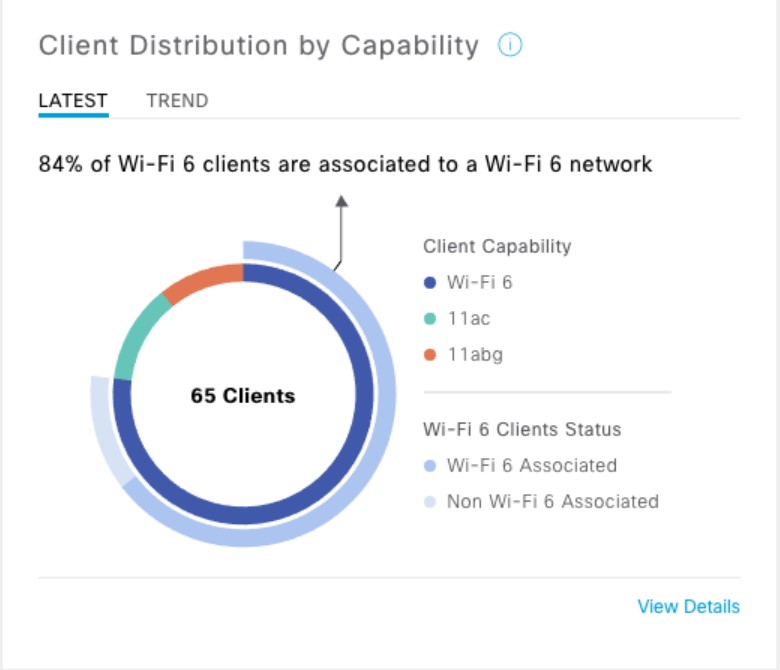
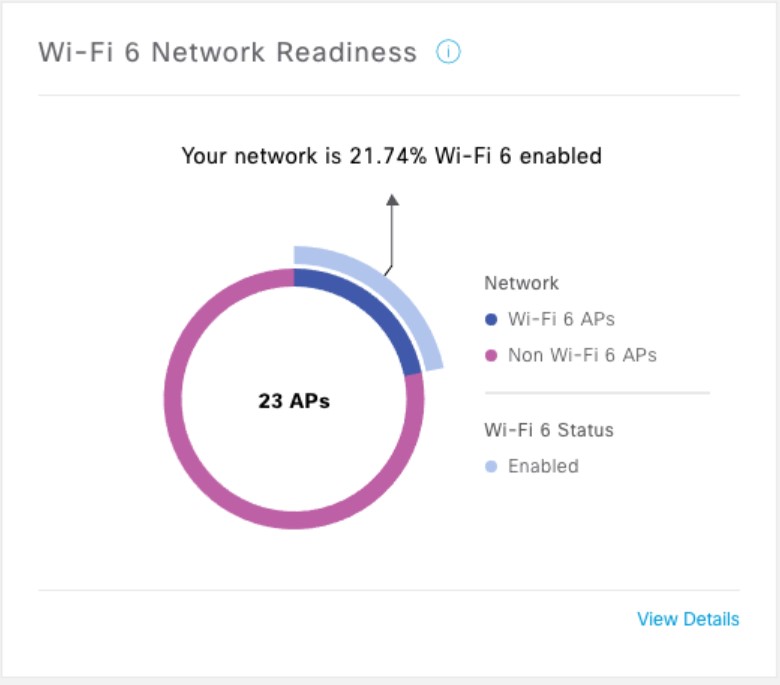
Cisco DNA Center is the foundational controller and analytics platform at the heart of Cisco’s intent-based network. It supports the expression of intent for multiple use cases, including base automation capabilities, fabric provisioning, and policy-based segmentation in the enterprise network. Cisco DNA Center brings context to this journey through the introduction of Analytics and Assurance by providing end-to-end visibility into the network with full context through data and insights.
About This Solution
Cisco DNA Center enables the network administrator to:
-
Design your network using intuitive workflows
-
Define user and device profiles that facilitate secure access and network segmentation based on business needs
-
Policy-based automation to deliver services to the network based on business priority and to simply device deployment
-
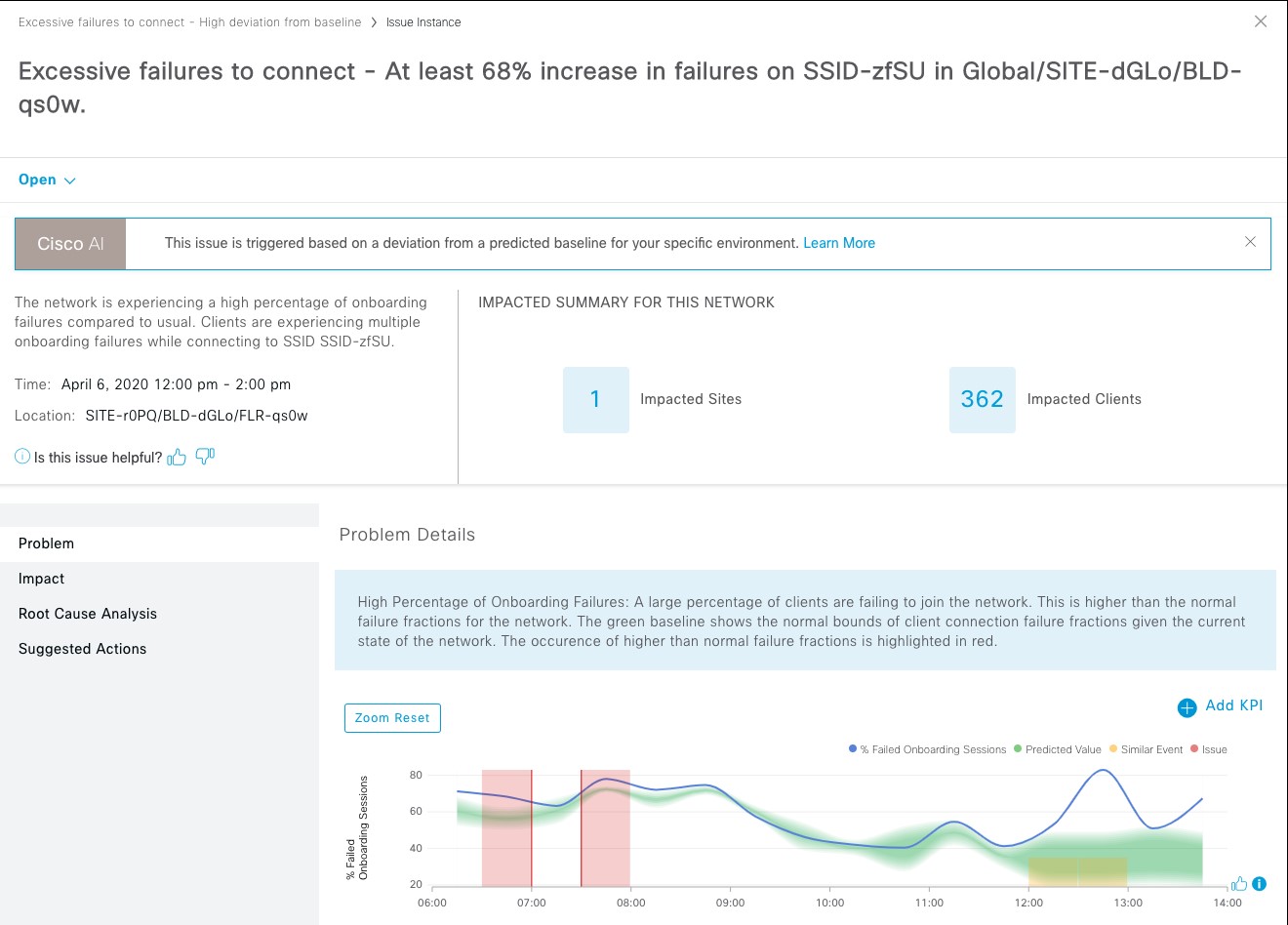
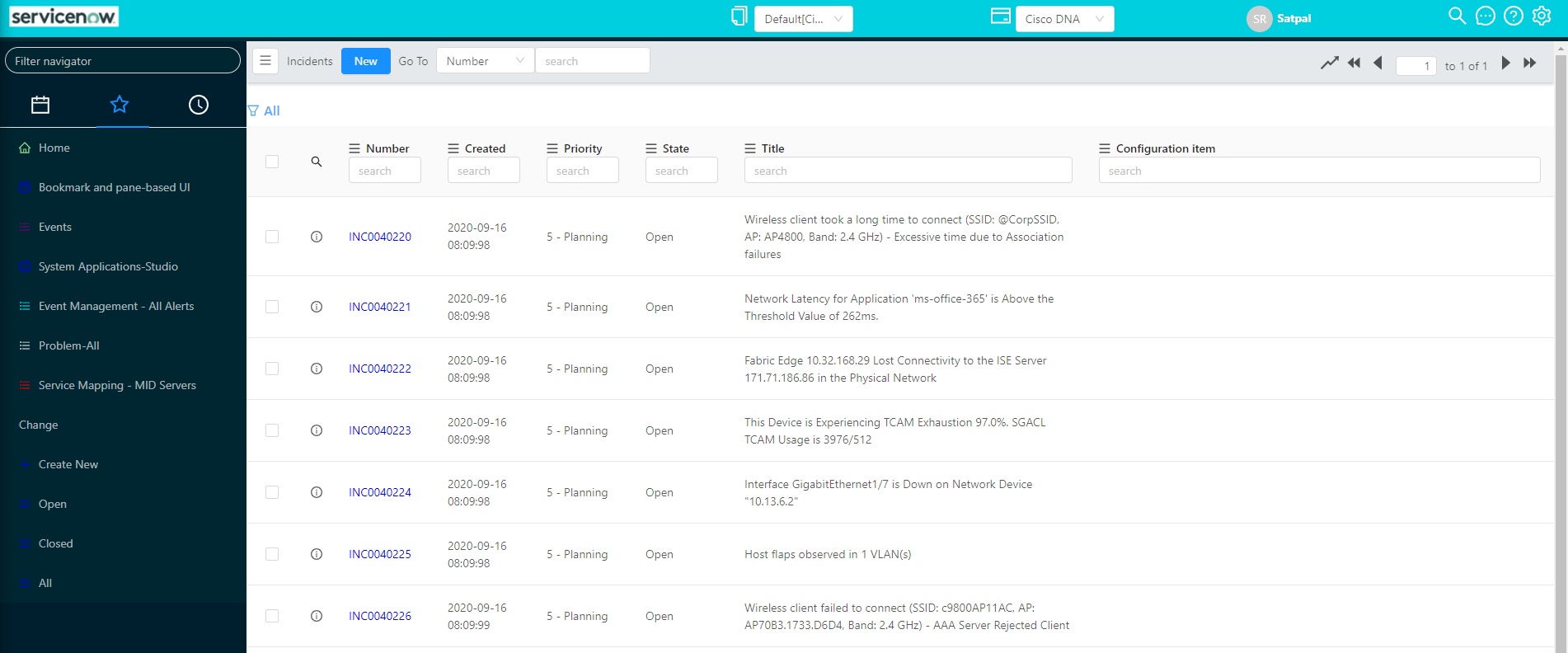
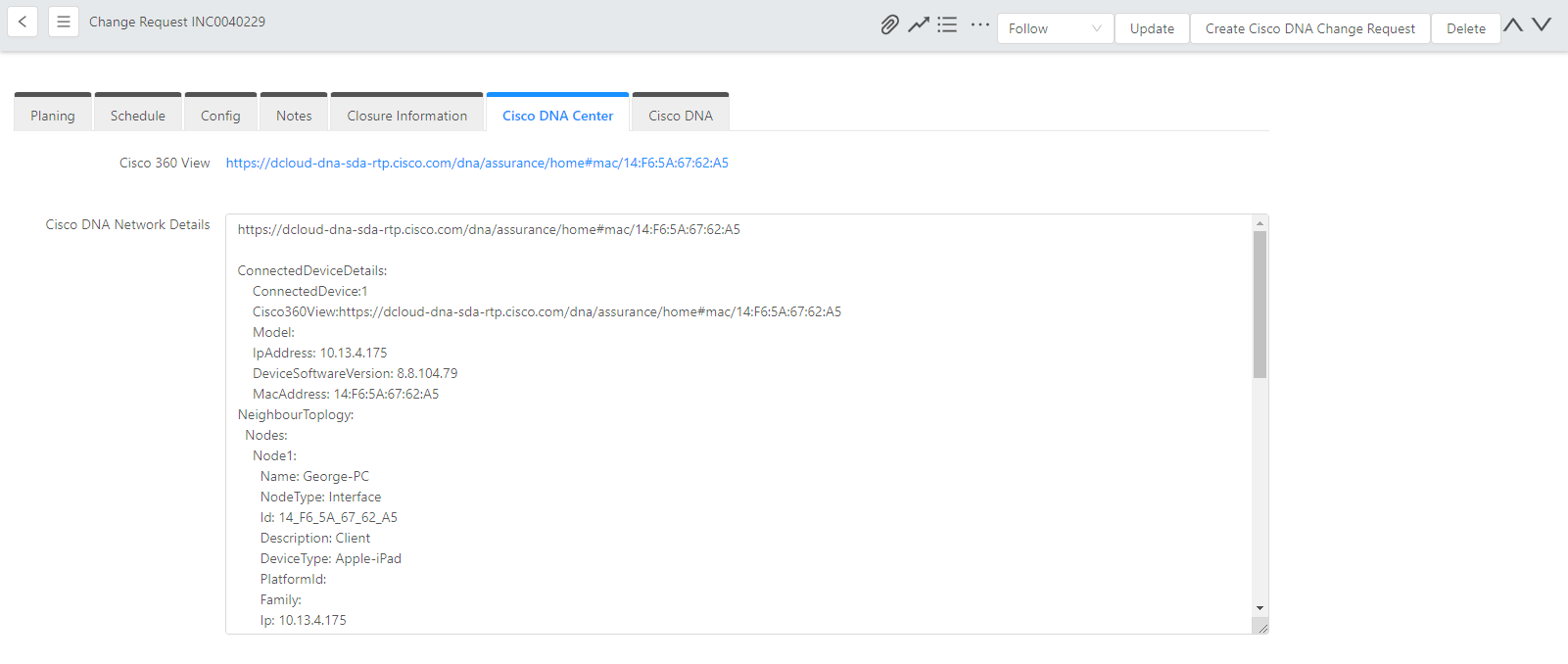
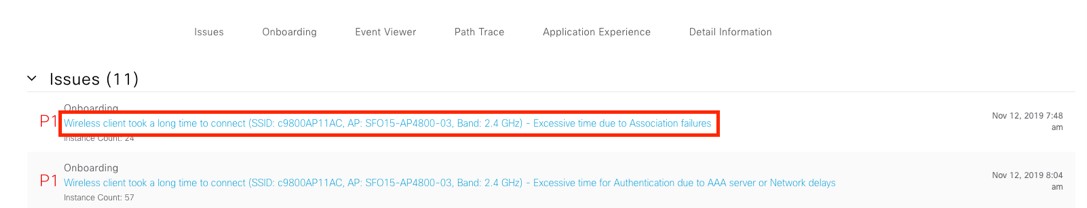
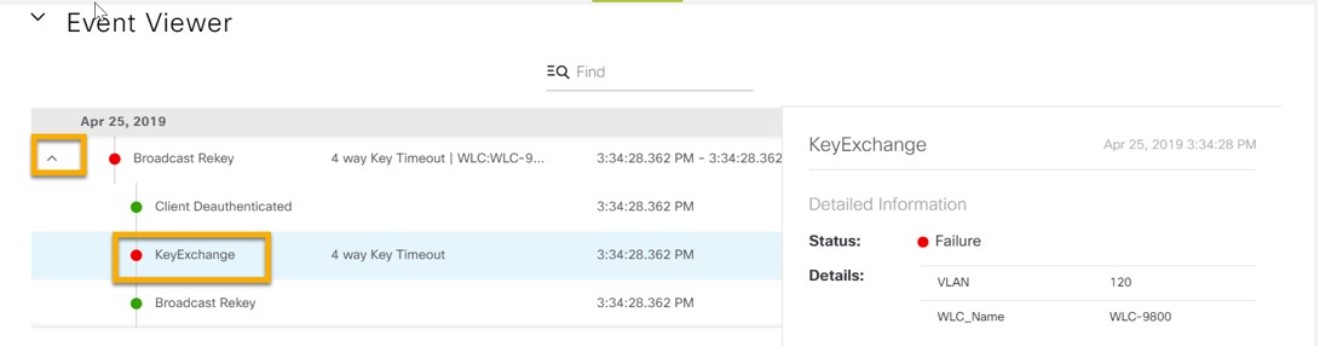
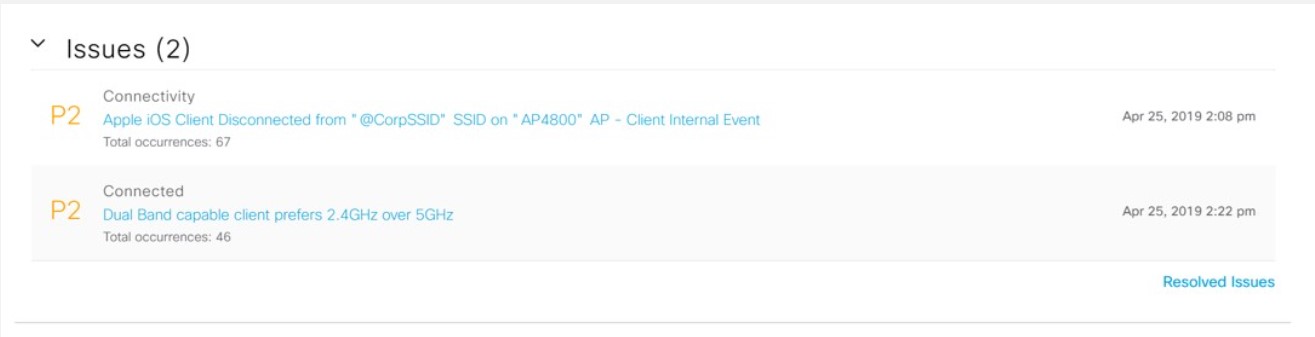
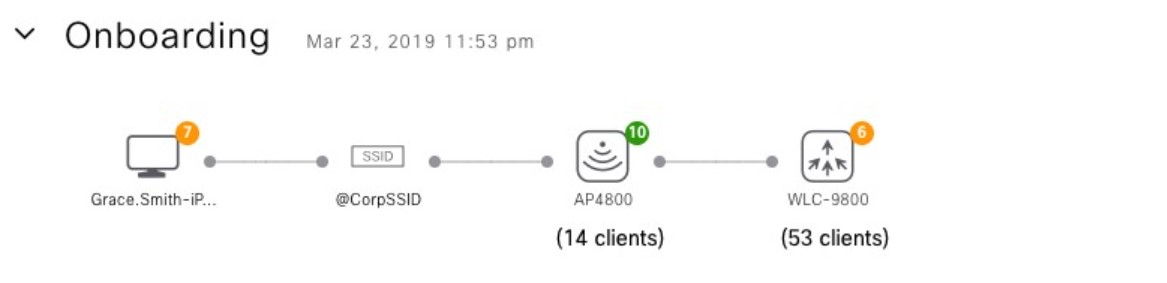
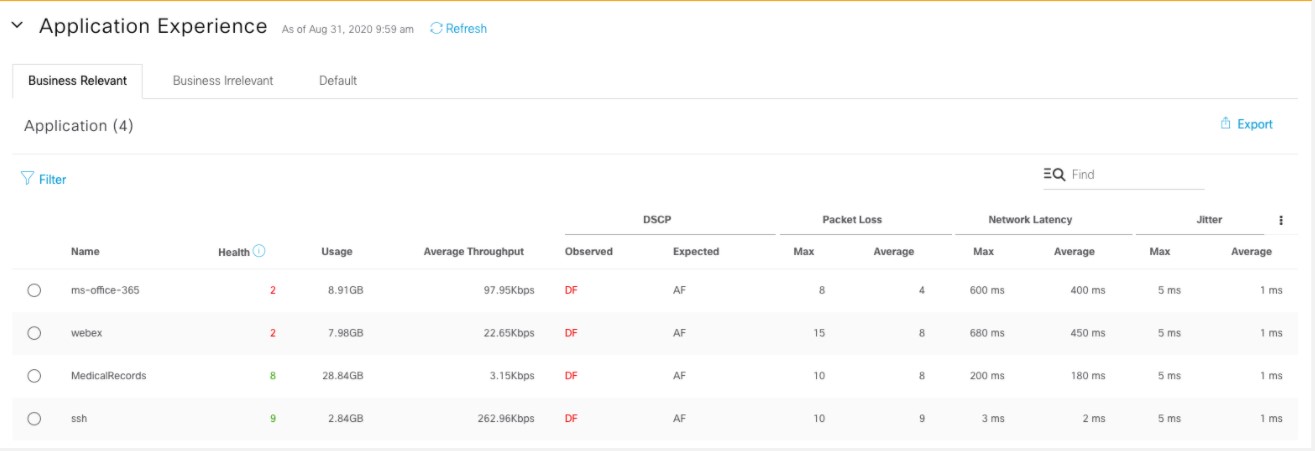
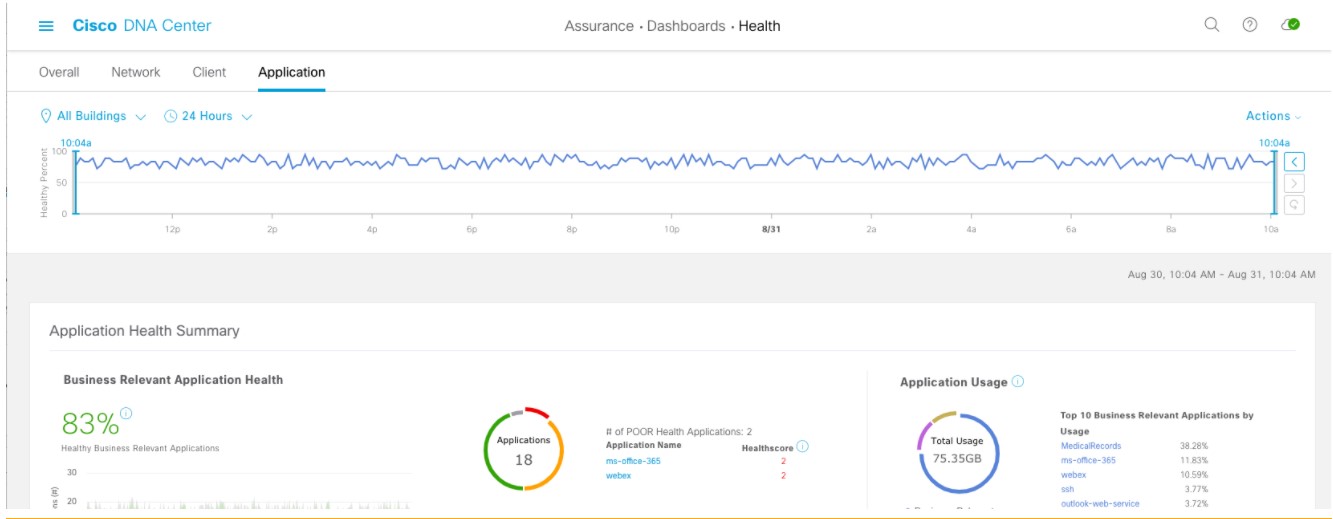
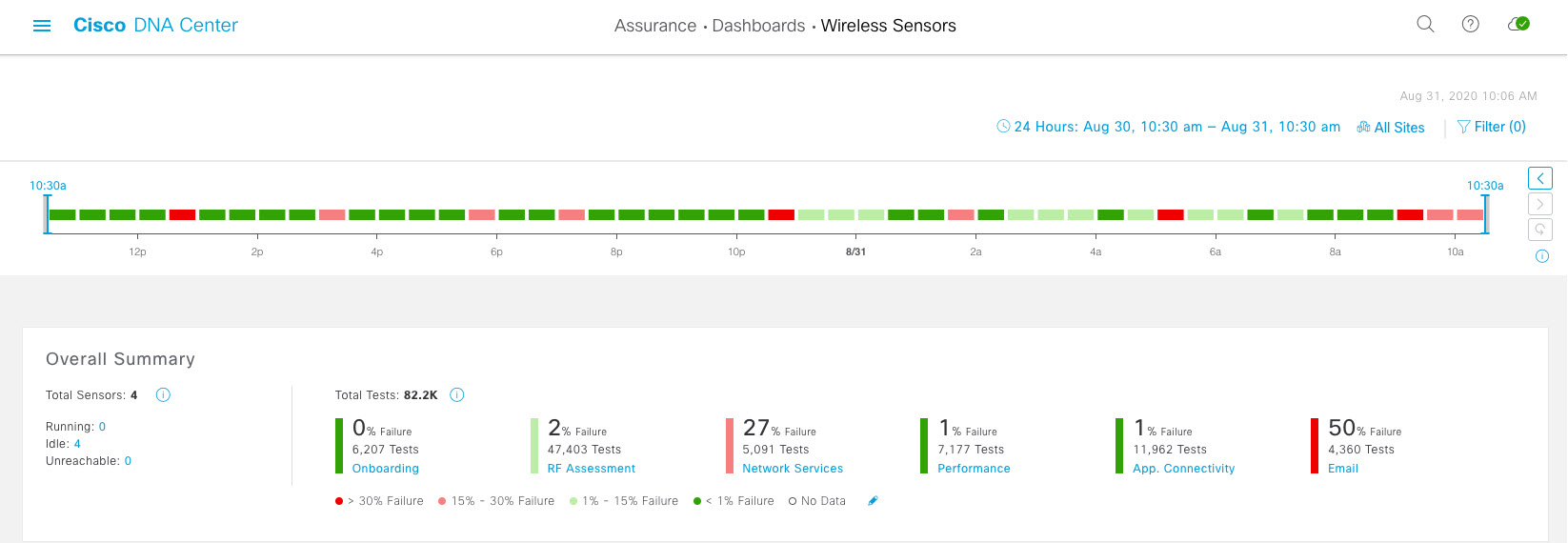
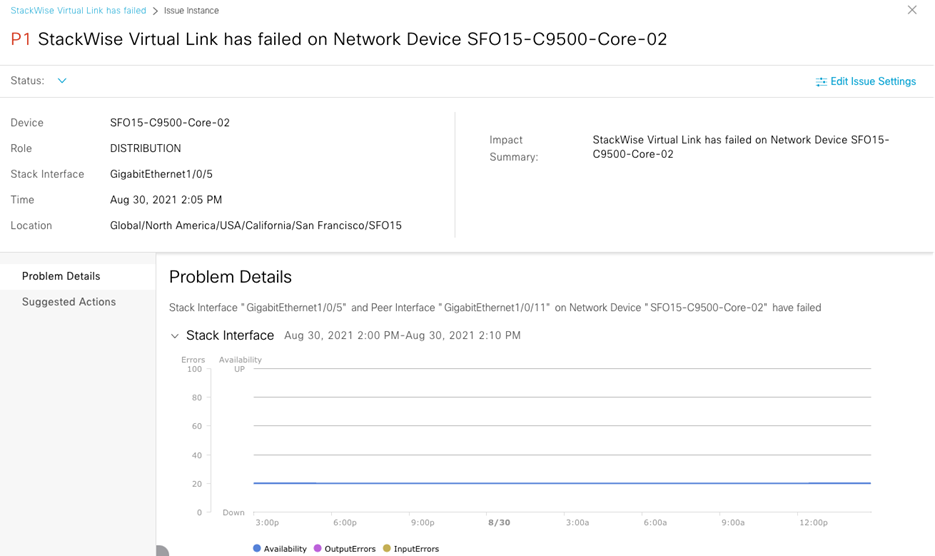
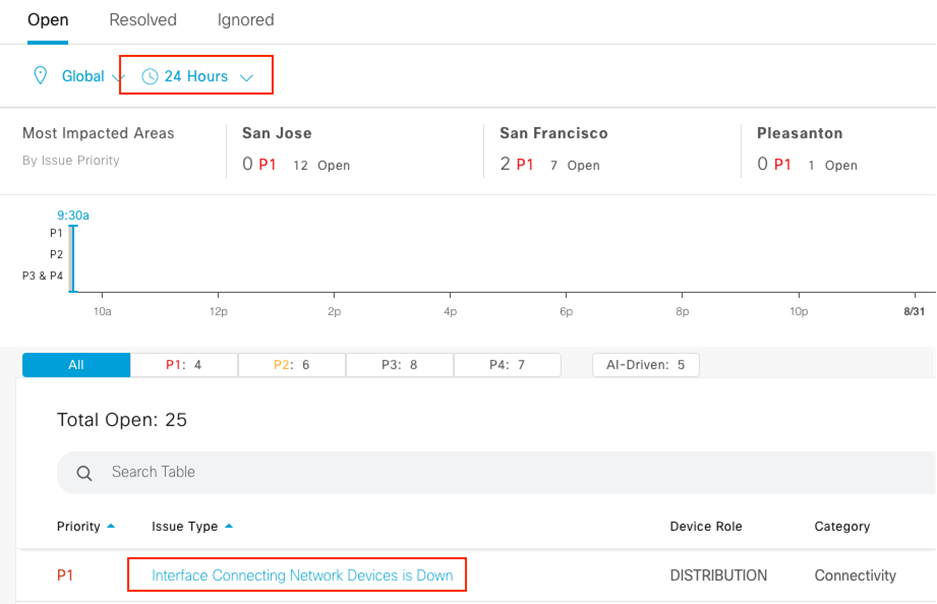
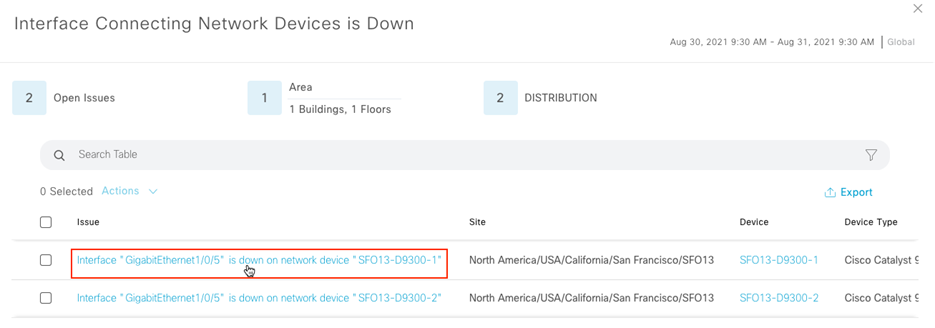
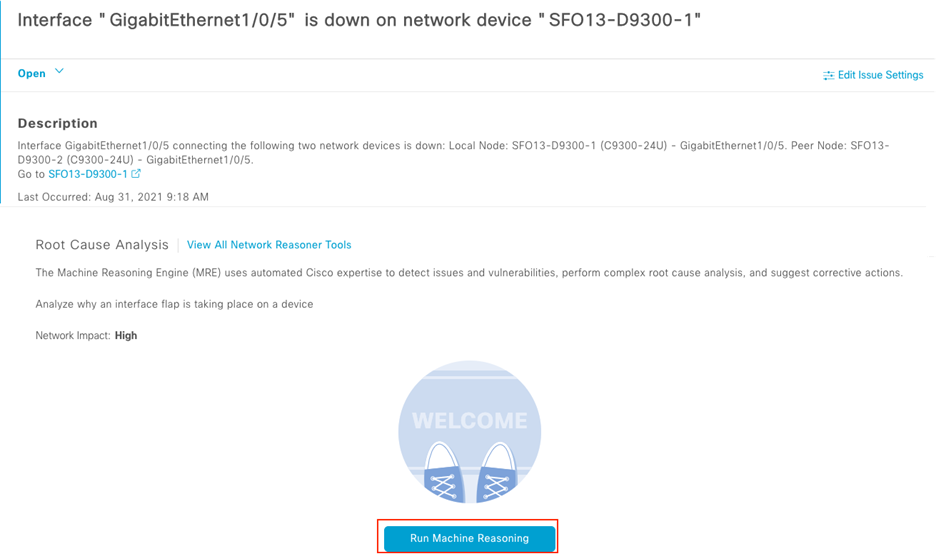
Assure network performance with real-time and historical data analytics, to provide actionable insights and detect problems before they happen along with Guided remediation actions for 100+ Insights
-
Design and Deploy Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) to simplifies delivery of consistent, highly secure, identity-based policy for users and devices across wired and wireless networks
This enables the network admin to have a simplified integrated user experience across the entire enterprise portfolio of products.